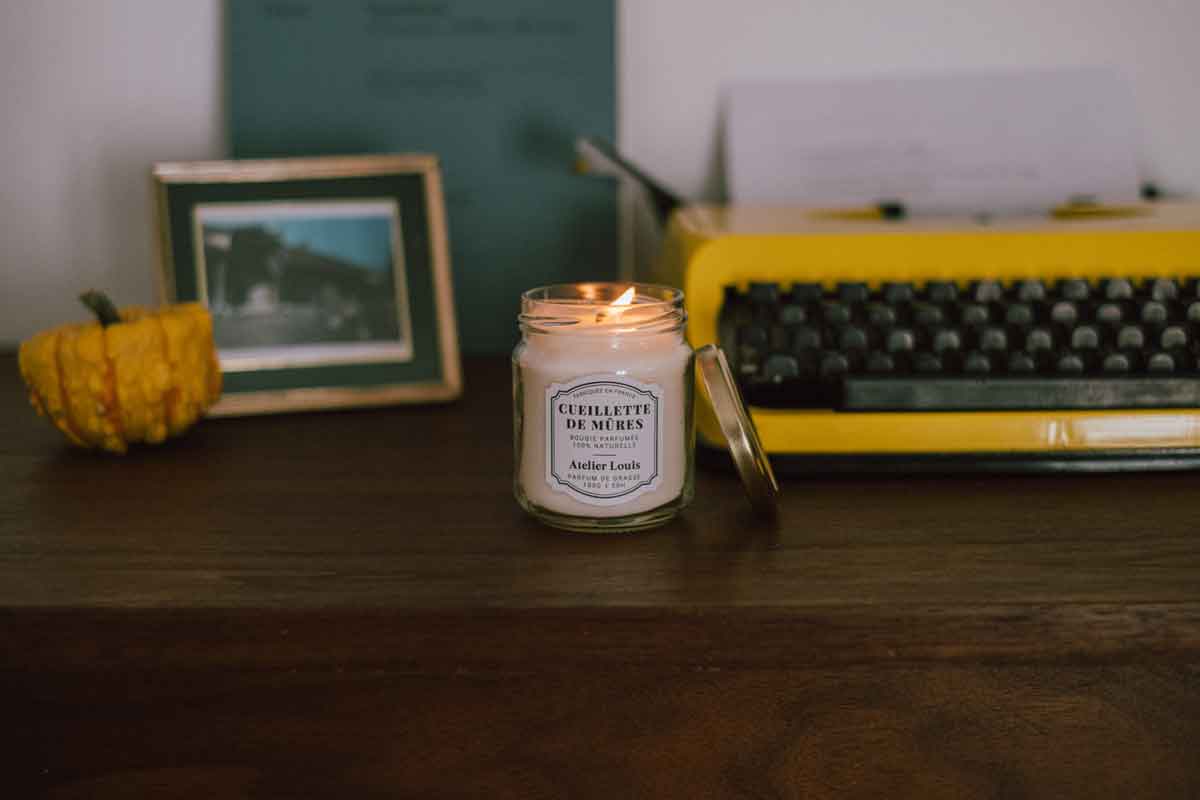
How does a scented candle burn?
The elements of a candle
Candles are much more than just decorative objects. They illuminate our living spaces and create a warm and soothing atmosphere. But have you ever thought about the science behind this soft light? Let's start by understanding the essential elements of a candle.
-
The Wick : It all starts with the wick, the thin piece of material in the center of the candle. Usually made of cotton, the wick plays a crucial role in the combustion process. It is through this that the heat necessary to melt the wax rises.
-
Wax : Wax is the main body of the candle. It can be made from a variety of materials, including paraffin, rapeseed wax, soy wax, beeswax, or other vegetable waxes. Wax is the fuel that burns slowly and produces light and heat.
-
Fragrance (optional) : In many scented candles, essential oils or perfumes are added to create a pleasant olfactory atmosphere.
The combustion process
Now that we know the basic components of a candle, let's explore how it burns.
When you light a candle wick, it begins to burn at one end. Here's what happens next:
-
The burning wick : The flame of the wick quickly heats the wax surrounding it. This heat melts the wax and turns it into a liquid.
-
Capillarity : The wick acts like a sort of lamp wick. The heat rises by capillarity, that is to say the melted wax is sucked by the wick to the upper part, where it evaporates.
-
Vaporization : As the wax evaporates, it turns into a gas and reacts with oxygen in the air. This creates a chemical reaction that produces heat and light, forming the flame we see.
What happens in a candle
Now that we know how a candle burns, let's dive a little deeper into the details of what's going on inside.
-
Combustion Zone : The area around the wick is the combustion zone. This is where there is enough heat to melt the wax and vaporize it, creating a flame.
-
Main Flame : The flame we see is the hottest part of the candle. It can reach temperatures of up to 1400 degrees Celsius (2500 degrees Fahrenheit)!
-
Internal Flame : Just below the main flame, there is a small, pale blue internal flame. This zone is rich in oxygen and is where the combustion reaction occurs most intensely.
-
Outer Flame : Around the inner flame, there is a yellow-orange outer zone. This part is slightly cooler than the main flame, which is why it appears different in color.
Understanding the burning process of a candle gives us a new appreciation for these small sources of light. The next time you light a candle, you'll know there's a lot more science and magic hidden behind that soft, calming light. Enjoy the ambiance it creates, while keeping in mind the complex process taking place inside.